The Global Software Testing Market in 2026: Strategic Imperatives for Digital Leaders
A Market Entering Its Next Growth Phase
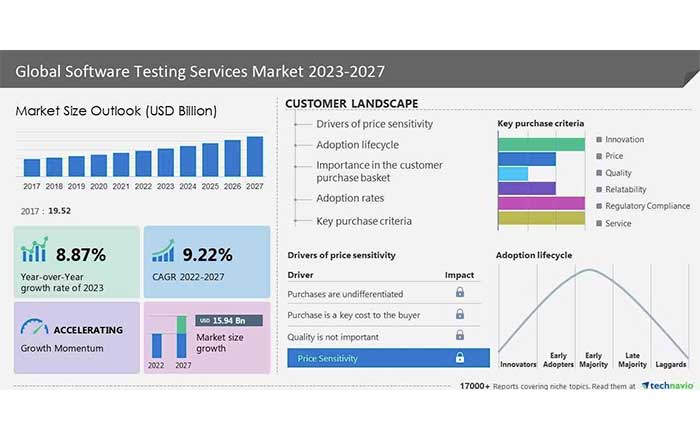
By 2026, the global software testing market has firmly established itself as a strategic pillar of digital transformation rather than a back-office technical function. Building on projections that anticipated an additional USD 16 billion in market value between 2024 and 2027, the sector is now expanding in lockstep with the accelerating adoption of cloud, artificial intelligence, mobile, and platform-based business models across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and emerging markets in Africa and South America. For enterprises in the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, Canada, Australia, Singapore, and beyond, software quality is no longer simply a matter of defect detection; it is a core component of brand reputation, regulatory compliance, cybersecurity resilience, and customer trust.
As FinanceTechX tracks these developments across fintech, banking, crypto, and the broader business landscape, it is clear that the organizations winning in this environment are those that treat software testing as a strategic capability. These leaders embed testing into product design, DevOps pipelines, and risk management frameworks, and they leverage global ecosystems of specialized vendors, crowdsourced communities, and AI-driven platforms to achieve scale, speed, and reliability simultaneously.
From Cost Center to Strategic Risk and Value Engine
Historically, software testing was often viewed as a necessary cost to be minimized. By 2026, that perception has shifted decisively. In financial services, healthcare, government, and critical infrastructure, regulators and boards increasingly recognize that software failures can trigger systemic risk, data breaches, and operational outages with cross-border impact. Regulatory bodies in key markets such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, the European Central Bank, and the Monetary Authority of Singapore have tightened expectations around operational resilience and technology risk management, reinforcing the need for robust testing practices. Organizations seeking to understand evolving regulatory expectations can review guidance from sources such as the Bank for International Settlements and the European Banking Authority, both of which emphasize the importance of reliable and secure digital infrastructure.
In this environment, testing serves as a bridge between technology execution and enterprise risk governance. Boards and executive teams increasingly request independent assurance on the robustness of test strategies, particularly for cloud migrations, open banking interfaces, algorithmic trading platforms, and AI models used in credit, fraud detection, or underwriting. This has elevated the role of Chief Technology Officers, Chief Information Security Officers, and Chief Risk Officers, who must collaborate to design testing regimes that cover functional accuracy, security, performance, data integrity, and regulatory compliance in an integrated manner.
Innovation Drivers: Crowdsourced, Automated, and AI-Enhanced Testing
One of the most transformative trends in the past few years has been the maturation of crowdsourced testing. This model mobilizes a distributed community of testers across continents, devices, and usage contexts to validate software in real-world conditions that are difficult to replicate in a traditional lab environment. Enterprises in Europe, North America, and Asia increasingly rely on crowdsourced testing for consumer-facing mobile apps, cross-border e-commerce platforms, and localized digital experiences. Crowdsourced approaches deliver output-based pricing, rapid turnaround, and broad device coverage, making them particularly attractive to fast-scaling digital-native firms and fintech startups featured on the FinanceTechX founders and world verticals.
Parallel to crowdsourcing, test automation has become foundational to modern software delivery. Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines are now standard across leading organizations, and automated regression suites, API tests, and performance tests are triggered on every code change. Artificial intelligence and machine learning have added a new layer of sophistication, enabling intelligent test case generation, self-healing test scripts, and anomaly detection in production telemetry. Technology providers and research institutions, including IBM, Microsoft, and leading universities referenced by resources such as MIT Technology Review, continue to explore how AI can reduce maintenance overhead and increase coverage without compromising reliability.
AI-enhanced testing is particularly relevant to the FinanceTechX AI and security audiences, as it intersects directly with model validation, bias detection, and adversarial resilience. As financial institutions deploy AI-driven credit scoring, wealth management advice, and fraud analytics, they must test not only the software pipeline but also the behavior of models under different data distributions and regulatory scenarios. Organizations seeking deeper perspective on responsible AI practices can review guidelines from bodies such as the OECD AI Policy Observatory and the World Economic Forum, both of which highlight testing and validation as central to trustworthy AI.
Core Testing Domains: Beyond Functional Correctness
The modern software testing market spans a wide spectrum of specialized domains, each necessary to deliver reliable digital services at scale. Functional testing remains the baseline, ensuring that applications behave according to specification, but enterprises have learned that functional correctness alone does not protect against real-world failures. Compatibility testing has become more complex as organizations target diverse device ecosystems across Android, iOS, web browsers, and embedded systems in markets from Japan and South Korea to Brazil and South Africa. Usability testing has moved closer to behavioral science, as firms analyze user journeys, accessibility, and conversion patterns using both qualitative and quantitative methods, often guided by standards such as the W3C Web Accessibility Initiative.
Security testing has expanded from traditional penetration testing to include continuous vulnerability scanning, secure code review, API security assessment, and red-teaming exercises. In sectors such as banking, payments, and digital identity, security testing is tightly coupled with compliance mandates such as PCI DSS, GDPR, and local data protection laws in jurisdictions including the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, France, and Singapore. Organizations can deepen their understanding of cyber risk and testing approaches through resources from ENISA, the National Institute of Standards and Technology, and industry groups like ISACA, which publish frameworks and best practices relevant to test and assurance functions.
Performance and load testing have also gained prominence as enterprises scale digital channels globally. Streaming platforms, online trading systems, and high-traffic e-commerce sites must withstand spikes in demand during peak events, from Black Friday and Singles' Day to IPOs and product launches. Failure to perform under load can erode customer trust and damage brand equity overnight. Enterprises increasingly simulate complex load patterns across regions using cloud-based tools, often integrating these tests into their ongoing DevOps workflows to detect regressions before they affect production.
Agile, DevOps, and the Rise of Continuous Testing
The adoption of Agile and DevOps methodologies has fundamentally reshaped how software testing is organized, executed, and governed. Rather than being a discrete phase at the end of development, testing is now integrated into every stage of the lifecycle, from design and architecture through deployment and operations. This shift, often referred to as "continuous testing," is particularly visible in high-velocity industries such as fintech, digital banking, and crypto-asset platforms, which FinanceTechX covers through its news and economy reporting.
In practice, continuous testing requires tight collaboration between developers, testers, operations teams, and security specialists. Testers participate in backlog refinement, define acceptance criteria, and design test strategies that align with business risk priorities. Automated tests run on every build, and quality gates prevent deployments that do not meet agreed thresholds. Observability tools collect telemetry from production, enabling teams to detect issues early and feed learnings back into test design. This feedback loop is particularly important for organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions, where user behavior, network conditions, and regulatory requirements vary widely across regions such as Europe, Asia, and North America.
DevSecOps extends this paradigm by embedding security considerations into the same pipelines. Static and dynamic application security tests, software composition analysis, and secrets detection are integrated into CI/CD workflows, ensuring that vulnerabilities are identified and remediated as part of everyday development rather than as a separate, late-stage activity. Security-conscious organizations can explore further guidance from initiatives like the Open Web Application Security Project, which provides widely recognized frameworks for secure software development and testing.
Cloud, Mobile, and the New Testing Perimeter
The rapid adoption of cloud-native architectures and mobile-first strategies has redefined the perimeter of testing. Modern applications are composed of microservices, APIs, third-party integrations, and serverless functions deployed across multiple cloud providers and regions. This complexity creates new failure modes and interdependencies that traditional testing approaches struggle to cover comprehensively. Enterprises in markets as diverse as the Netherlands, Switzerland, China, India, and New Zealand are increasingly turning to cloud-based testing platforms that can provision environments dynamically, simulate distributed systems, and support large-scale tests without heavy capital investment.
Mobile-based testing has become particularly critical in regions where smartphones are the primary access point to digital services, including Southeast Asia, Africa, and parts of Latin America. Testing strategies must account for varying device capabilities, operating system versions, network quality, and localization needs. In some markets, such as Thailand, Malaysia, and South Africa, the diversity of devices and connectivity conditions makes real-world testing via crowdsourced communities especially valuable. Organizations looking to understand broader digital inclusion and connectivity trends often refer to data from sources like the International Telecommunication Union, which tracks adoption patterns that directly influence testing priorities.
At the same time, cloud-based testing introduces new security considerations. Test data management has become a board-level concern, as organizations must ensure that sensitive production data is not exposed in test environments, particularly when working with external vendors or crowdsourced testers. Privacy-by-design principles, data masking, synthetic data generation, and strict access controls are now essential elements of responsible testing practice. Regulatory expectations in jurisdictions such as the European Union, the United States, and Singapore reinforce this need, and enterprises frequently reference guidance from regulators and privacy watchdogs when designing their test data strategies.
Talent, Skills, and the Evolving Role of the Tester
As the software testing market has matured, the profile of testing professionals has changed significantly. Manual testing skills remain relevant, particularly in exploratory, usability, and domain-specific scenarios, but organizations increasingly seek testers who can code, understand system architecture, and collaborate closely with developers and product owners. Test automation engineers, performance specialists, security testers, and AI testing experts are in high demand across global hubs such as London, New York, Berlin, Toronto, Sydney, Singapore, and Tokyo.
This talent evolution has important implications for the job market, which FinanceTechX tracks through its jobs and education coverage. Organizations compete for scarce expertise, while professionals invest in continuous learning through certifications, online courses, and community participation. Global training providers, universities, and industry associations, including those highlighted by platforms such as Coursera and edX, have expanded their curricula to cover test automation, DevOps, security testing, and AI-driven quality engineering.
In many enterprises, the role of the tester has evolved into that of a quality engineer or quality coach. These professionals influence architecture decisions, define quality metrics aligned with business outcomes, and help teams design tests that reflect real-world risk scenarios. In regulated sectors such as banking and insurance, testers also interact with compliance and audit teams, contributing to documentation and evidence required for regulatory reviews. This convergence of technical, business, and regulatory skills underscores why testing is now viewed as a strategic career path rather than a purely operational role.
Market Structure and Leading Vendors
The software testing market remains highly fragmented, with a mix of global service providers, niche specialists, and platform vendors competing for enterprise budgets. Large technology and consulting firms such as Atos SE, Capgemini, Cognizant Technology Solutions Corp, Infosys Ltd, Tata Consultancy Services Ltd, Wipro Ltd, and International Business Machines Corp offer end-to-end testing and quality engineering services, often integrated with broader digital transformation, cloud migration, and managed services offerings. These organizations leverage economies of scale, global delivery centers, and deep domain expertise in sectors such as banking, telecommunications, manufacturing, and public sector.
Alongside these giants, a vibrant ecosystem of specialized vendors has emerged. Companies including DeviQA Solutions, Expleo Group SAS, Hexaware Technologies Ltd, Kualitatem Inc, Oxagile, QA Mentor Inc, QA TestLab Solutions Ltd, QASource, QualiTest Group, QualityLogic Inc, TestFort, and LogiGear Corp focus on specific niches such as test automation, performance engineering, security testing, mobile testing, or industry-specific solutions. Many of these firms differentiate themselves through proprietary accelerators, domain knowledge, and flexible engagement models tailored to the needs of startups, scale-ups, and mid-market enterprises.
For executives evaluating potential partners, independent research and advisory firms play a crucial role. Technavio, for example, has built an extensive library of technology market reports covering software testing trends, vendor landscapes, and regional dynamics across more than 50 countries. Organizations can complement such insights with perspectives from other leading analysts and professional bodies, including Gartner, Forrester, and IDC, to form a holistic view of vendor capabilities and market evolution.
Sustainability, Green IT, and Responsible Testing
As environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations gain prominence in boardrooms worldwide, the software testing community is beginning to confront questions about the environmental footprint of digital infrastructure and testing practices. Large-scale test environments, performance simulations, and continuous integration pipelines consume significant computing resources, which in turn contribute to energy usage and carbon emissions. For organizations committed to sustainable business practices, understanding and optimizing the environmental impact of testing has become part of broader green IT strategies.
This development intersects closely with the FinanceTechX focus on environment and green fintech. Cloud providers, including hyperscale players, have started to publish more granular data on the carbon intensity of their regions and services, enabling enterprises to make informed choices about where and how they run their tests. Industry initiatives and research from organizations such as the Green Software Foundation offer guidance on designing energy-efficient software and test environments, while broader sustainability frameworks from bodies like the United Nations Environment Programme encourage companies to integrate digital sustainability into their overall ESG strategies.
Responsible testing also encompasses ethical and social dimensions. As AI systems and digital platforms influence credit decisions, employment screening, healthcare access, and public services, testing teams must consider fairness, explainability, and inclusivity. This means designing test cases that cover diverse user groups, edge cases, and potential sources of bias, and collaborating with legal, compliance, and ethics teams to align testing practices with organizational values and societal expectations.
Strategic Considerations for Business and Technology Leaders
For the global audience of FinanceTechX, spanning executives, founders, investors, and technology leaders from the United States and Europe to Asia-Pacific and Africa, the implications of the evolving software testing market are both operational and strategic. At an operational level, organizations must ensure that their testing capabilities keep pace with the complexity and velocity of modern software delivery. This often requires investments in automation, tooling, skills, and partnerships, as well as the integration of testing into DevOps and cloud-native architectures.
At a strategic level, leaders must recognize that testing is central to several board-level priorities: digital transformation success, cyber resilience, regulatory compliance, customer experience, and ESG commitments. Decisions about where to build in-house capabilities versus where to partner, how to govern quality across business units and geographies, and how to measure the return on investment in testing will shape competitive advantage over the coming years. Resources such as the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund provide macroeconomic context that influences technology investment cycles, while FinanceTechX continues to analyze how these trends play out across stock exchange listings, venture funding, and M&A activity in the testing and quality engineering space.
Looking Ahead: Testing as a Foundation for the Next Digital Decade
As the global software testing market moves through the latter half of the 2020s, its trajectory is intertwined with broader technological and economic shifts. The expansion of 5G networks, edge computing, quantum experimentation, and advanced AI will introduce new testing challenges and opportunities in regions from Scandinavia and the Benelux countries to China, India, and Latin America. Governments and regulators will continue to refine rules around digital resilience, privacy, and AI governance, further elevating the importance of rigorous testing and validation.
For organizations that follow FinanceTechX across its homepage and specialist channels, the message is clear: software testing is no longer a peripheral technical activity but a core enabler of trustworthy, resilient, and sustainable digital business. Enterprises that invest in modern testing practices, cultivate skilled quality engineering talent, and build strategic partnerships with leading vendors and research bodies will be better positioned to navigate uncertainty, seize new opportunities, and maintain the confidence of customers, regulators, and investors in an increasingly software-defined world.